|
|
INTODUCTION |
 |
This pamphlet is written for you cancer patients it also
may be useful for members of your family. We believe it is important for you and
yours family to understand yours illness so you can face it together, with courage
and hope. Much has been learned about the nature of cancer in recent year’s .as
a results, strides have bee made in diagnosing the disease and treating it effectively.
These modern Methods are described this pamphlet. |
|
|
|
CANCER OF THE LUNG |
|
|
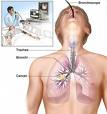
Your lungs are part of the respiratory system which enables
you to breathe. Lungs look like pinkish-gray. Spongy tissue. Your right lung is
a little larger then your left and has three sections. Or lobes. Your left lung
has two lobes, and your heart takes up some of the room on the left side of your
chest. The air in hale from your mouth or nose goes through breathing to tubes,
or passages, and branches into the main air passages of the lung called bronchi.
One bronchus goes to the right and one to the left lung. Your bronchi branch in
to smaller tubes that carry air to all parts of your lung. They end in clusters
of tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Lungs cancer, like other cancer, is an expression of the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells.
Most lung cancers begin on the bronchi (the larger air
tubes) or the brounchioles (the smaller tubes branching of the bronchi). Normally
cells grow in an orderly, controlled pattern m. As normal cells wear out, new once
are produced. Just enough new cells grow to replace the old ones.
Cells of each part of your body such as your bones, skin
and heart differ in shape and function, each type of cell is designed to do a particular
job in a particular organ.
When cell division is not orderly, abnormal growth takes
place. Masses of tissue called tumors build up. Tumor may be benign or malignant.
Benign tumors remain localized and usually do not spread or threaten once life.
They can be removed completely by surgery and are not likely to recur.
Malignant tumors are cancer. They can invade and destroy
nearby tissues and organs or, spread to other part of the body. The new growths
they from in other parts of the body are called metastases. Even if cancer is removed
by surgery or radiation therapy, it may be some times recur because cancer cells
have spread before having begun treatment of the local disease.
|
|
|
SYMPTOMS |
|
|
A cough, the most common symptom of hung cancer, is likely
to occur when a growing cancer blocks airway. You cough as if you where trying to
get rid of a foreign object stuck in your lungs. In some cases your saliva is stiked
with rusty or even bright red blood.
Another symptom is chest pain. It occurs as apersistent
ache that might or might not be related to coughing.
You may develop a wheeze, or hoarseness, or find yourself
short of breath. Repeats bouts pneumonia or bronchitis, to may be an indication
of lung cancer and. Like all cancers, lung cancer can cause fatigue, loss of appetite.
And weight loss.
In addition, there may be symptoms that seem entirely
unrelated to the lung. These may be caused by spread of a lung cancer to other part
of the body.
When you see your doctor, you should report all aches
or pains. They may be important clues.
|
|
|
|
DIAGNOSIS |
|
|
|
Diagnosis begins with a physical examination by your doctor.
There are a number of test he may use to confinn a suspected diagnosis of lung cancer
and to determine the type of the dieses.
Chest x-ray are important in detecting lung cancer. In
addition to the conventional chest X-ray number of other X-ray procedures is available
to assist the diagnosis, such as tomograms, bronchograms, and angiograms.
Lung tomograms are special chest x-ray, perfected some
years ago. A tomogram is a series of pictures of various sections of lung tissue.
When these pictures are put together, they
give a three-dimensional picture of any abnormal lungs growth. If the tomograms
suggest that a lump is cancerous, additional studies are needed to narrow down the
dignosis.
More recently, a newly developed type of tomogram, called a “CAT” scan
(computerized axial tomography) has on occasion proven to be helpful.
Bronchograms outline the inside of lung passages and may show tumors that are otherwise
invisible.
Angtograms, X-ray studies of blood vessels II, made visible with an injected dye,
can reveal a displacement of a vein or artery by tumors.
Your doctor recognize distinctive. Characteristics of cancer that determine whether
microscopic examination of a specimen of tissue from the suspected area should be
made. The surgical removal of small amount of tissue and its examination under a
microscope is known as a biopsy. The examination of the bit of tissue removed is
made by a changes caused by disease in the body tissues. |
|
|
|
